Juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA) is a group of rheumatic diseases that affect children under the age of 16. It is characterized by persistent or recurrent joint inflammation. This inflammation can have devastating effects on the child's quality of life. So, as a parent, understanding the origins, symptoms, and treatments of JIA is essential to help your child in his quest for a fulfilled life.
What is juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA)?
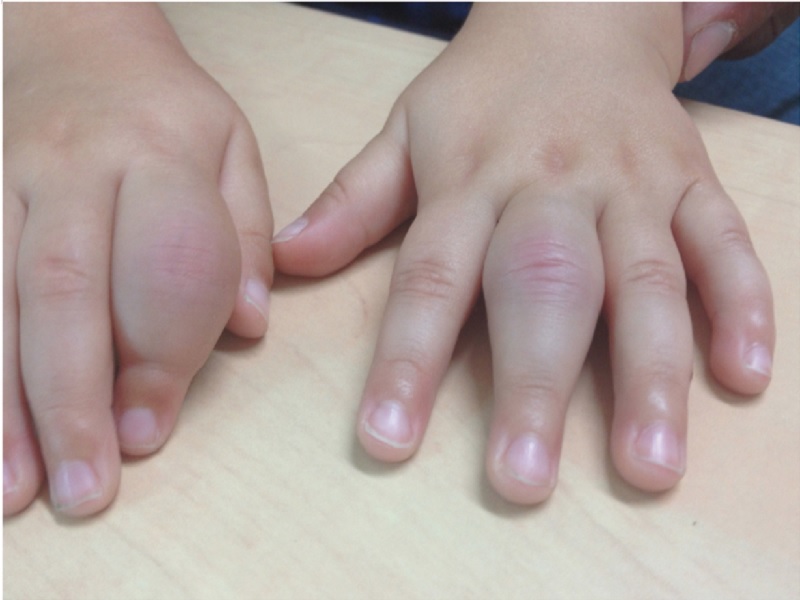
JIA is a chronic inflammatory joint disease that develops in children under the age of 16. This chronic condition causes pain, joint stiffness, and functional limitation.
Juvenile idiopathic arthritis is a complex disease that requires a multidisciplinary approach for the management of symptoms.
Possible causes of juvenile idiopathic arthritis
The precise causes of JIA remain unknown. However, there are certain factors that increase the risk of developing the disease, including :
- Genetic factors: Some studies have shown that variations in certain genes can increase susceptibility to the disease.
- Environmental Factors: Viral or bacterial infections could trigger JIA in some genetically predisposed people.
- Dysfunction of the immune system: A faulty immune system regulation in genetically predisposed children could lead to joint inflammation, potentially linked to JIA.
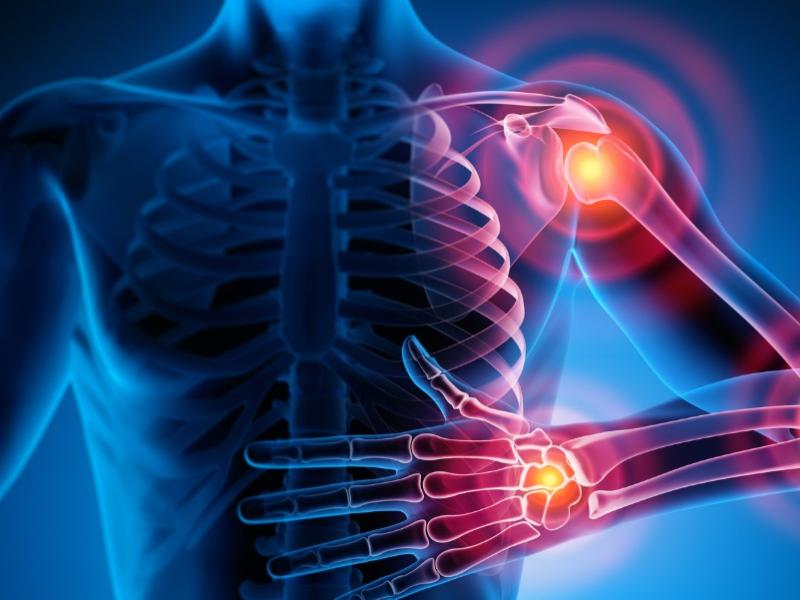
What are the symptoms of JIA?
The symptoms of JIA can vary from a child to another, but common signs include:
- Persistent or intermittent joint pain
- Morning stiffness
- Swelling of the joints
- Fatigue
- Fever
- Loss of appetite
If your child has any of these symptoms, it is important to consult a doctor for an accurate diagnosis.
How is JIA diagnosed?
The diagnosis of JIA is based on a combination of tests, including :
- Blood tests.
- Medical imaging examinations (such as X-rays).
- The evaluation of clinical symptoms.
Your doctor will also examine your child's medical history to rule out other possible causes of the symptoms.
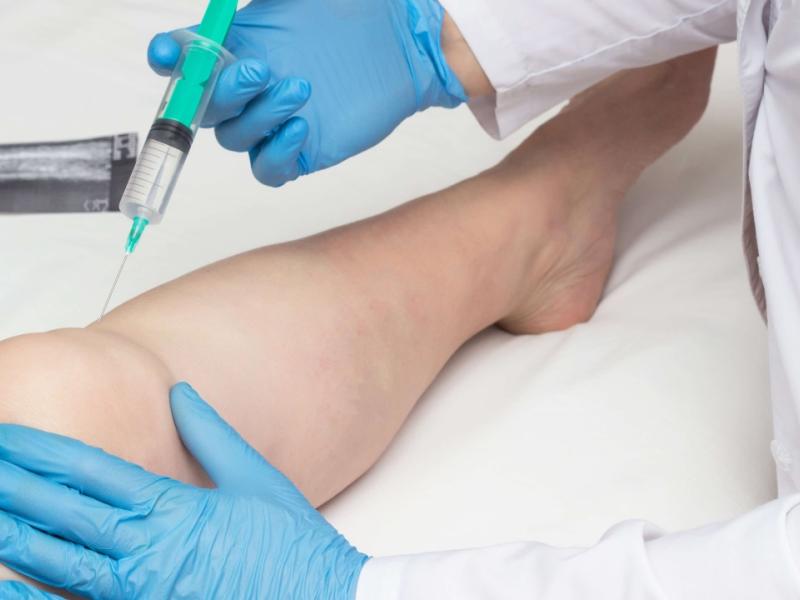
What are the treatments available for JIA?
The treatment of JIA aims to reduce inflammation, prevent joint damage, and improve the child's quality of life. Treatment options may include :
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to relieve pain and inflammation.
- Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) to slow the progression of the disease.
- Biological drugs to target specific proteins involved in inflammation.
- Physical therapy and occupational therapy to maintain joint mobility.
- Dietary adjustments to support your child's overall health.
How can you support your child with JIA?
As a parent, your support plays an essential role in managing your child's JIA. Here are some tips to help you :
- JIA can be an emotionally difficult experience for your child. So, be sure to offer him attentive listening and acknowledge his feelings.
- Find out as much as possible about JIA: The more you know about the disease, the better you will be able to support your child and make informed decisions about his treatment.
- Encourage a healthy lifestyle: A balanced diet, regular exercise and enough rest are important to manage JIA. Find ways to make these aspects of life healthy, and fun for your child.
- Be open to communication with health professionals. Be sure to ask all your questions and concerns during medical consultations. Open and honest communication will help you make the best decisions for your child.
- Seek support from organizations and support groups dedicated to parents of children with JIA.