What is Dermatitis (Eczema)?
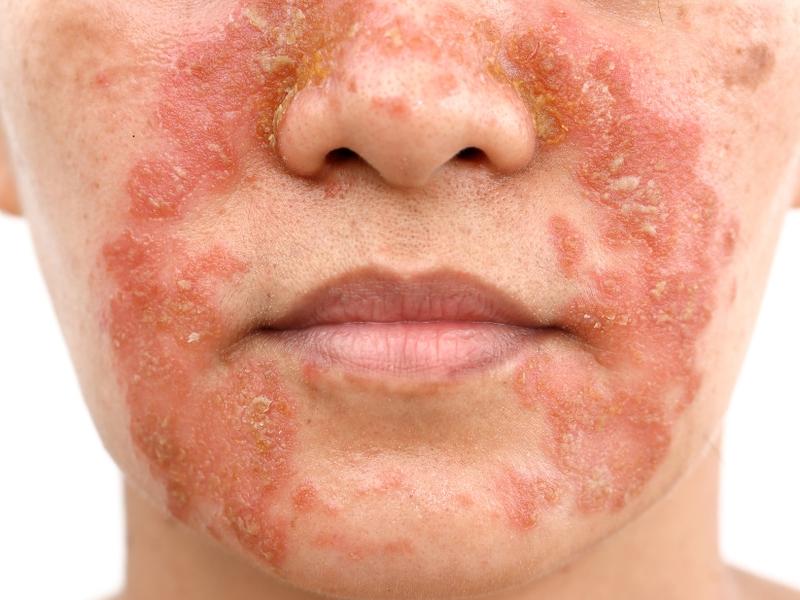
Dermatitis (or eczema) is an inflammation of the superficial layers of the skin, accompanied by redness, itching, and swelling, caused by irritation or an allergic reaction to external or internal factors.
It may be of different types (atopic, seborrheic, allergic, irritant) and may be transient or persistent, depending on the case. It can also be accompanied by scaling, vesicles, blisters, erosion, and crusts.
Dermatitis symptoms: how to recognize them?
The most common symptoms of eczema include :
- The appearance of papules, vesicles, and patches on the skin
- Redness of the affected area, accompanied by a sensation of heat and burning
- Increased dryness of the skin
- Progressive scaling
- Intense itching that causes the patient to scratch frequently
- Presence of abrasions and scabs on the skin
Atopic Dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis is the most common form of eczema. It is a chronic and recurring inflammation of the skin that causes itchy skin and visible redness.
It affects many parts of the body, including the hands, face, knees, elbows, and scalp. Likewise, it most often appears at birth with a severe cradle cap. But a sudden onset can occur in adolescents and adults.
Some studies have shown that the causes may include a hereditary genetic component, but also air pollution or the adoption of excessive hygiene practices.
Seborrheic Dermatitis
Seborrheic dermatitis is characterized by skin inflammation affecting areas of the skin rich in sebaceous glands, including the scalp, nasolabial folds, retro auricular areas, superciliary arches, and sternal areas.
In its mild form, seborrheic dermatitis is manifested by the appearance of red and scaly patches. When the dermatitis is more severe, it can also manifest itself as erythematous patches covered with yellowish-greasy scales.
The reasons that lead to the appearance of seborrheic dermatitis are not fully understood. Nevertheless, an excessive proliferation of Malassezia yeast, frequently present on the skin, may be responsible for the scaling and inflammation.
In addition, seborrheic dermatitis may be exacerbated by other factors, such as
- Hormonal imbalances (especially during climatic changes)
- Psychophysical stress
- Genetic predisposition
Allergic Contact Dermatitis
Allergic contact dermatitis is an allergic skin reaction that occurs when the skin comes into contact with an irritant or allergen (chemical or natural). This contact triggers an immunological response and an inflammatory reaction that develops and causes itching.
Allergic contact dermatitis can affect any part of the body with a single allergen, such as hair dye on the scalp or nickel on the earlobes and palms.
Irritant contact dermatitis
Irritant contact dermatitis is an inflammation of the skin caused by certain chemical and physical stimuli. It usually affects areas such as the hands, neck, and face that are exposed to external contact, although a typical irritant dermatitis is diaper rash, which affects the skin area covered by the diaper due to prolonged contact with feces and urine.
Some of the most common triggers include:
- Surfactants, alcohols, and antiseptics contained in detergents.
- Solvents, acids, alkalis, glass wool, etc.
- Substances released by certain plants.
Treatment of Dermatitis
Treatment of dermatitis varies depending on the clinical variant observed.
The main goal of treatment is to relieve the symptoms of the disease by using saline compresses and emollient creams or lotions.
Cortisone may be used in the worst cases. Keep in mind, however, that the use of cortisone is not a permanent solution to the problem of dermatitis. In fact, this treatment has a short-term effect and does not protect the patient from possible relapses or negative effects related to its excessive use.
Since there is no real cure for dermatitis, it is preferable to act directly on the daily factors that can aggravate or reappear in the condition, in addition to the therapies prescribed by the dermatologist. It is therefore advisable to consult a specialist in dermatology in Turkey, who will be able to give the right advice on the practical steps to be taken to effectively combat the disease.