What is a dental fistula?
A dental fistula is a visible channel through which pus, often from an untreated tooth infection, can drain into the surrounding tissue.
There are two types of fistulas:
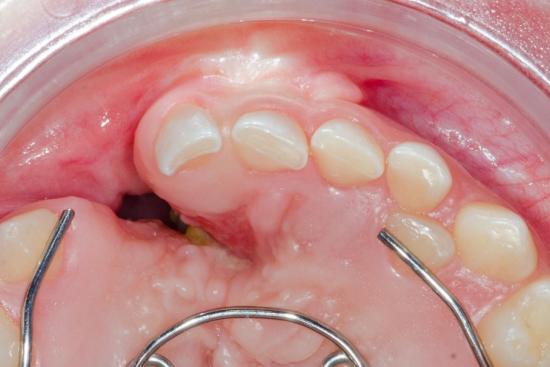
- Intra-oral (internal) fistula: When it opens onto the buccal or gingival mucosa.
- Extra-oral (external) fistula: When it opens onto the cheek.
Causes of dental fistulas
Dental fistulas can be caused by a variety of pathologies:
- Dental abscess: an accumulation of pus caused by a bacterial infection in the jaw or gums.
- Untreated dental caries: damage to the teeth caused when bacteria in the mouth produce acids that attack the tooth enamel.
- Dental fractures: Damage to tooth structure often caused by trauma, decay, or grinding.
- Impacted wisdom teeth: when they do not emerge properly in the dental arch.
- Chronic periodontal disease, especially periodontitis.
To avoid fistula complications, you should seek immediate medical attention at the first sign of a dental infection.
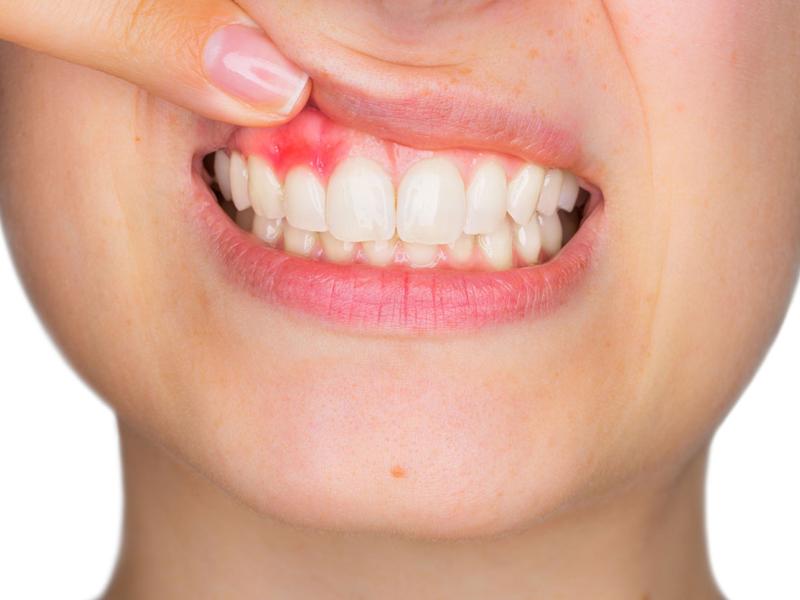
Symptoms of dental fistulas
Apart from the exit orifice, which is a more or less visible lesion in the mouth or on the skin, dental fistulas have relatively few symptoms. These symptoms vary according to the location and severity of the fistula. The most common symptoms include:
- Swelling.
- Redness.
- Pus discharge from the affected area.
- Sharp pain.
- Fever.
- Bad breath and taste in the mouth.
In many cases, the infection can spread to other parts of the body and become life-threatening.
Treatments for dental fistulas
Treating a dental fistula usually involves draining the abscess and treating the underlying infection with antibiotics.
In more severe cases, root canal therapy or tooth extraction may be necessary to remove the source of the infection.
Some dental fistulas may require surgery to drain the abscess and remove any pus. This is especially true for fistulas that are accompanied by infection of the surrounding soft tissues.
How can I prevent dental fistulas?
Good oral hygiene is essential to maintaining healthy teeth.
To prevent dental fistulas, here are the best practices you should follow:
- Brush regularly 2 to 3 times a day.
- Use dental floss and interdental brushes.
- Biennial dental checkups and cleanings.
- Limit your intake of sugary foods and tobacco to reduce the risk of gum disease and plaque buildup.
If you suspect a fistula, see your dentist or periodontist. Early treatment can prevent complications and help maintain good oral health.