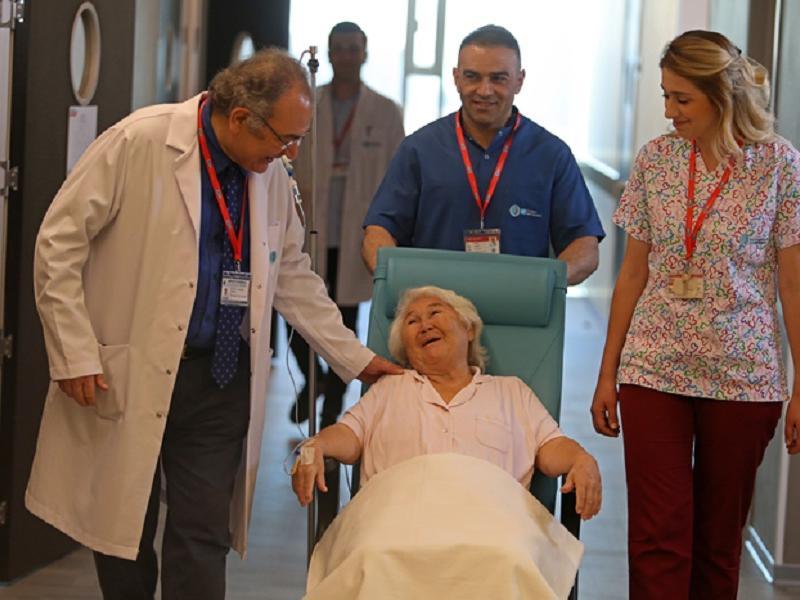
Oncologic surgery is a medical specialty dedicated to the surgical treatment of cancer. It intervenes at different stages of the disease, from confirmation of the diagnosis to management of recurrences.
In Turkey, surgical oncologists work closely with other healthcare professionals (physicians, radiation oncologists, medical oncologists) to develop an individualized and optimal treatment plan for each patient.