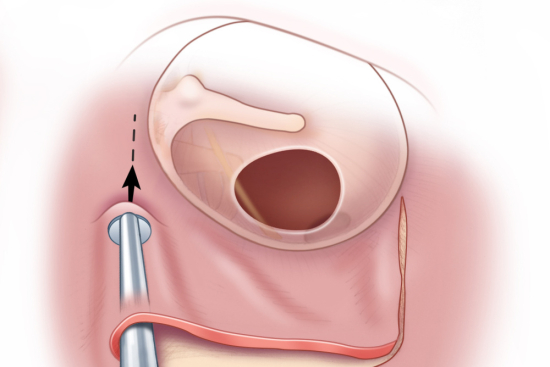
Tympanoplasty in Turkey is a reconstructive surgery to repair a perforated eardrum or rebuild the middle ear. The eardrum, or tympanic membrane, is a thin wall that separates the outer ear from the middle ear. In the middle ear are three small bones called ossicles that respond to sound vibrations and transmit them to the inner ear, where the hearing process is located.
Price of eardrum repair in Turkey
The cost of tympanoplasty in Turkey varies depending on the complexity of the procedure. A tympanoplasty combined with ossicular reconstruction is generally more expensive than a simple tympanoplasty.
You should remember that price is not the only factor to consider when choosing a clinic for tympanoplasty in Turkey. Quality of care and your safety are also important factors to consider.
In general, the price of a tympanoplasty in Turkey is between €2,000 and €4,000. This price includes the hospital stay, anesthesia, and the surgeon's fees.
Thanks to Turquie Santé, specialized ENT doctors will get back to you within minutes.
Request a free personalized quote from the best ENT specialists in Turkey.