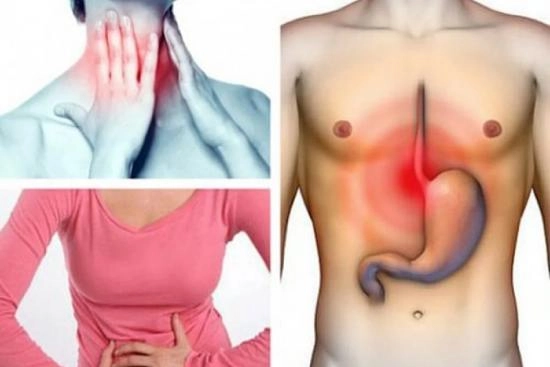
Do you often feel a burning sensation in your chest after eating? It could be gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD),a common condition caused by the backflow of stomach juices into the esophagus. This phenomenon is usually associated with a malfunction of the lower esophageal sphincter, which doesn't close properly after meals.
These episodes should not be taken lightly if they occur more than once a week. Chronic GERD can lead to complications and requires accurate diagnosis. Many specialized clinics in Turkey offer comprehensive evaluation and customized treatment in a modern environment.